Three Russian Navy amphibious warfare ships departed the Baltic Sea, headed toward the Atlantic Ocean, as tensions continue to surround Moscow’s build-up of troops and equipment around its borders with Ukraine.
A separate flotilla of three Russian landing ships had previously been the cause of recent alarm in Sweden, which sent additional forces to the island of Gotland, in the Baltic, in response to the increased Russian maritime activity in the region.
De tre RUPUCHA klasse gik under broen. Billeder fra FB gruppen “Under Broen” – og tak for dem.
The trio of vessels that left the Baltic today and are headed for an unknown destination comprise Project 775 Ropucha class amphibious warfare ships. All three, the Korolev, Minsk, and Kaliningrad, are seen in the Tweets embedded above.
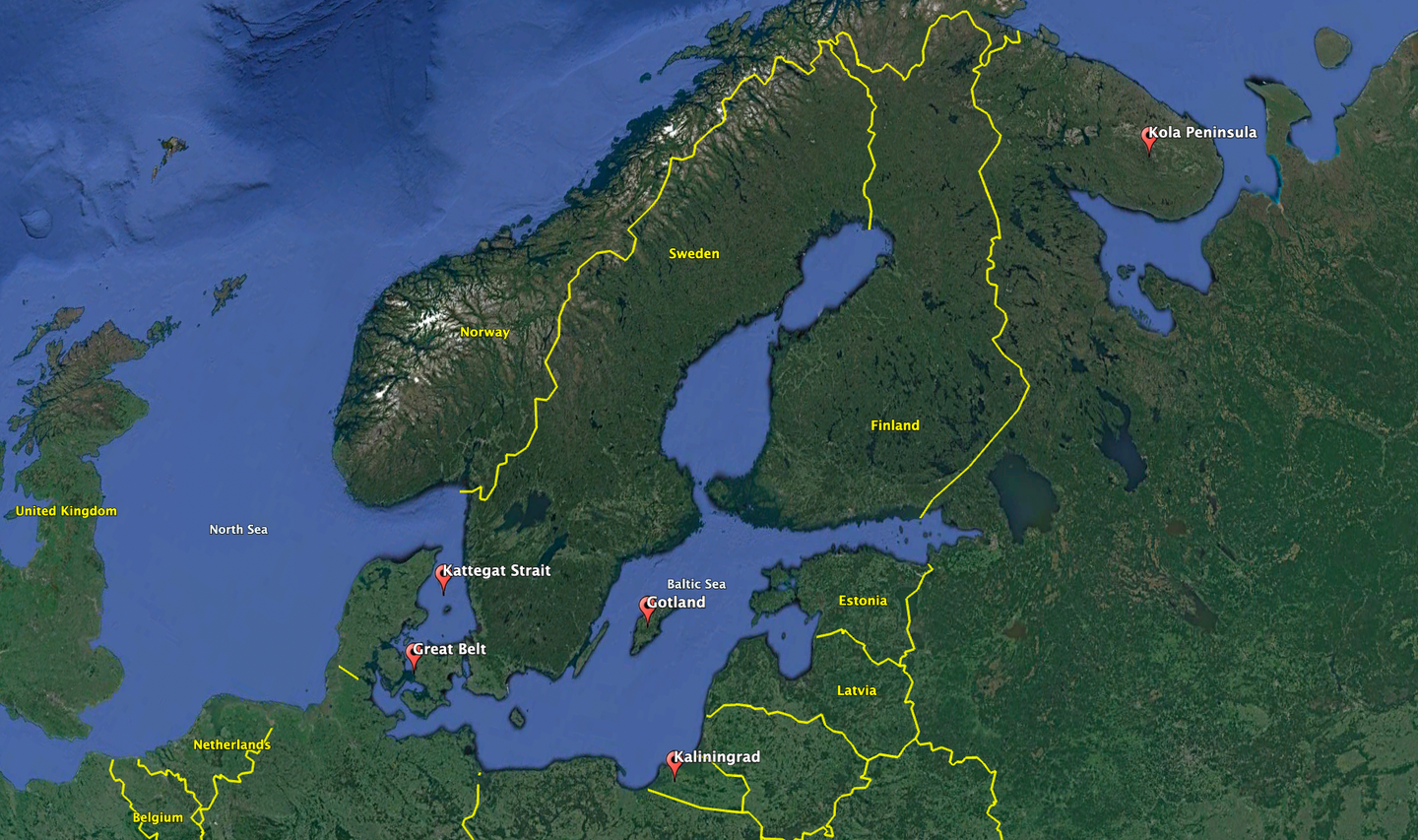
They departed the port of Baltyysk in the Russian exclave of Kaliningrad on January 15 and earlier today passed through the Great Belt, the largest of the straits that connect the Baltic to the Kattegat strait and which then leads to the Atlantic Ocean.
While naval transits, including those involving landing ships, to and from Kaliningrad are by no means uncommon, Swedish officials have made clear that the current level of activity is unusually high.
It appears that Western maritime patrol and surveillance aircraft have been keeping an eye on the Russian naval presence in the Baltic. A U.S. Navy P-8A maritime patrol aircraft was noted operating off the Danish coast and over the Baltic today, while a Swedish Air Force S 100D Argus airborne early warning and control aircraft has also been active in the region today, according to open-source flight data.
The transit of the three Baltic Fleet Ropuchas leaves two Northern Fleet vessels of the same class in the Baltic. These are the Olenegorskiy Gornyak and Georgiy Pobedonosets. Those ships were accompanied there by the Project 11711
Ivan Gren class landing ship Pyotr Morgunov last week.
GOOGLE EARTH
Each Ropucha class ship can carry up to 10 main battle tanks and 340 troops, 550 tons of cargo, or equivalent loads. The more modern Ivan Gren class can carry up to 13 main battle tanks and around 300 troops. It’s unclear what, if any, cargo the vessels are currently carrying.

The Russian Navy landing ship Pyotr Morgunov during the celebrations for Navy Day in 2020., Russian Government
The three Northern Fleet vessels had traveled from their home port on the Russian Kola Peninsula, sailing along the coast of Norway and then entering the Baltic via the Danish Strait on January 12.
During their passage, the ships were monitored by the Swedish Air Force, including by Gripen fighter jets.
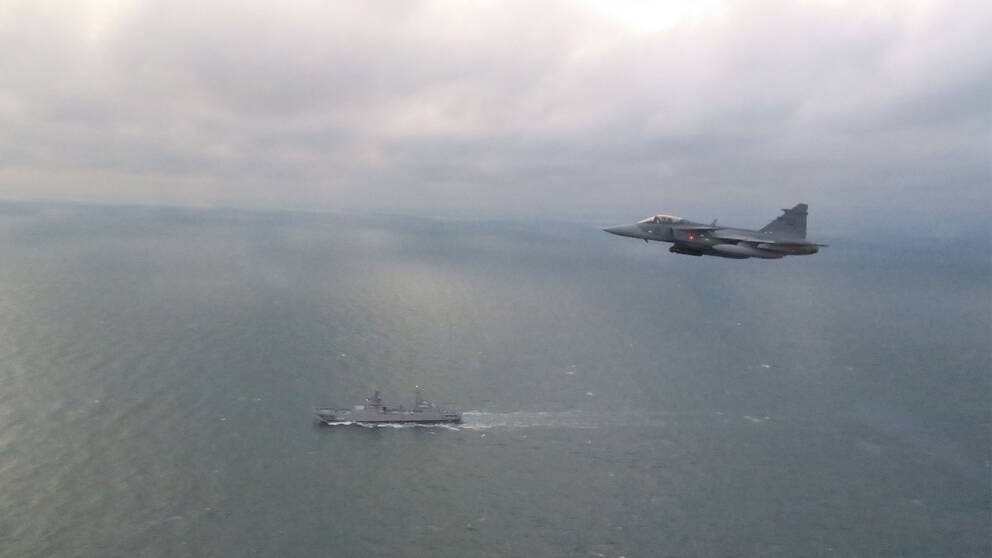

A Swedish Air Force JAS 39C Gripen keeps watch on a Russian landing ship underway in the Baltic., Swedish Armed Forces
“We have different types of sensors and systems that help us monitor the ships,” said Therese Fagerstedt, a press secretary for the Swedish Armed Forces. “We have also been able to follow them via our pilots in the air force and take pictures.
“We are always interested in movements in our immediate area, and this in itself is nothing out of the ordinary,” Fagerstedt added.
“But given the growing tensions in the immediate area, we wanted to follow up and monitor these ships. We also do this to give our commanders a good basis for any decisions on measures from the Armed Forces.”
The Swedish Armed Forces had already increased readiness in response to a perceived deterioration in the security situation in the Baltic Sea last year.
Last August, Swedish armored vehicles were transported by civilian ferry to Gotland, the island occupying a strategic position in the Baltic, as another signal to Russia over its expanded military activity in the region.
However, the recent appearance of the three Northern Fleet vessels prompted Sweden late last week to deploy hundreds of troops to once again reinforce Gotland. The troops were brought from the mainland using a combination of aircraft and passenger ferries.
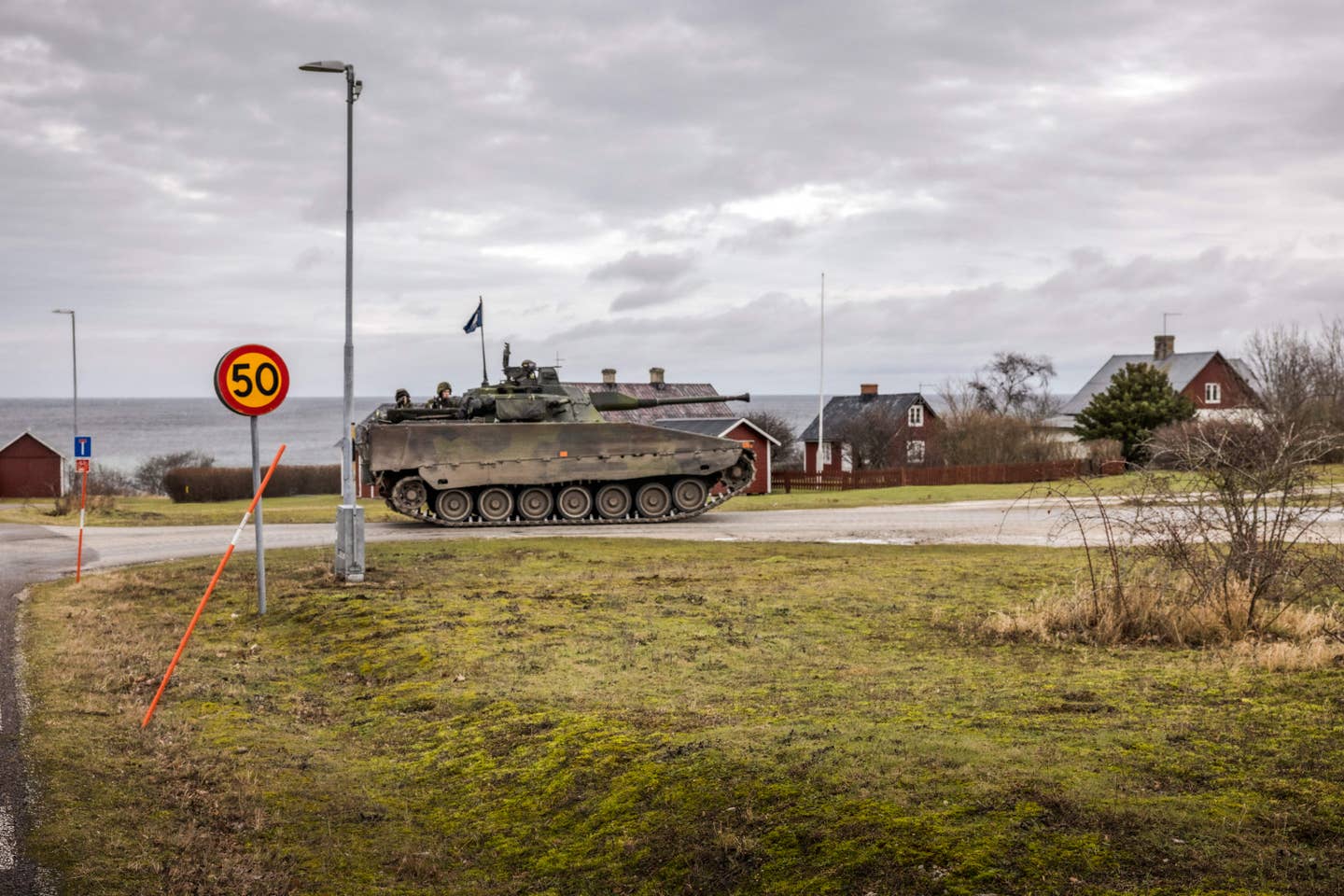

A Stridsfordon 90 armored vehicle from the Gotland Regiment on patrols in northern Gotland on Jan. 16, 2022., KARL MELANDER/TT News Agency/AFP via Getty Images
As well as the Russian naval activity in the Baltic, the Swedish response has considered the security situation elsewhere in Eastern Europe, above all along Ukraine’s borders with Russia. Here, an influx of Russian troops and materiel have led to widespread concerns that Moscow is poised to launch a potential new invasion of its neighbor.
“It is clear there is a risk [to Gotland],” the Swedish Minister of Defense Peter Hultqvist explained at the weekend. “An attack against Sweden cannot be ruled out. … It’s important to show we are not naive. Sweden will not be caught napping if something happens. It is important to send signals that we take this situation seriously.”
At the same time, Sweden has been looking into the mysterious appearance of unidentified drones, which appeared in its airspace over multiple nuclear power facilities, on Jan. 14. An investigation into the incident, which The War Zone
covered at the time, is now underway.
Denmark, too, has recently announced additional military measures in response to what it has determined to be Russian threats toward Ukraine.
The country will deploy four F-16 fighter jets to Šiauliai Air Base in Lithuania, while the frigate Peter Willemoes will be made available to NATO’s naval forces and is expected to patrol the Baltic Sea. Both deployments are due to begin before the end of the month.
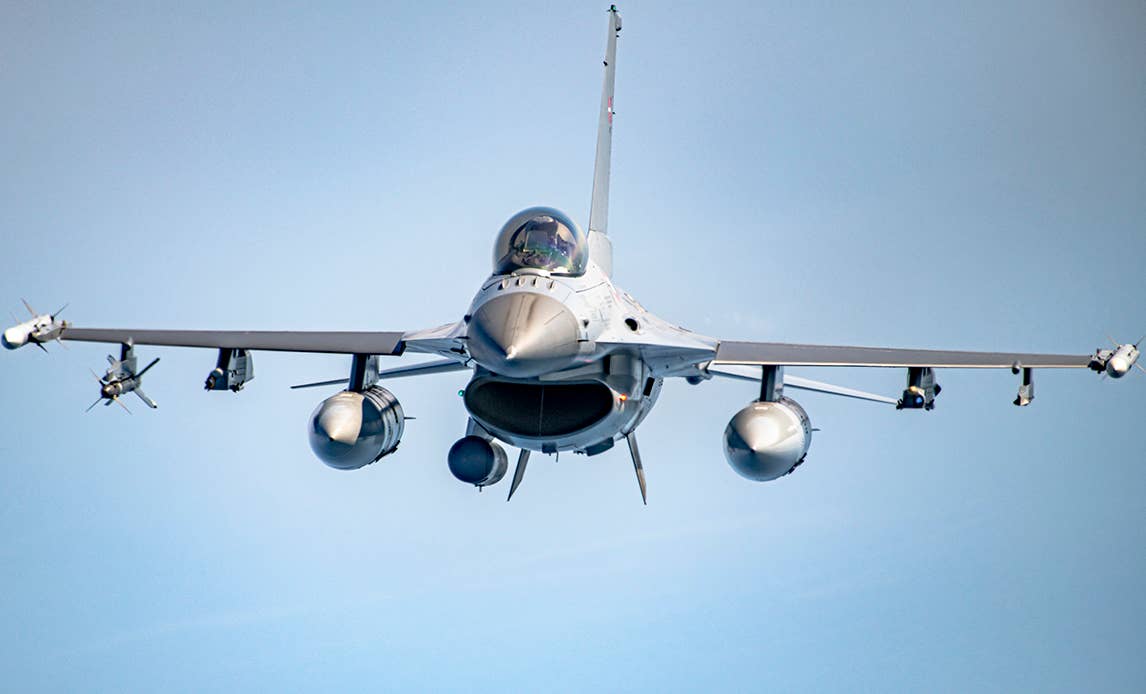

A Royal Danish Air Force F-16AM fighter jet armed for an air policing mission., Rune Dyrholm/Forsvaret
“We have a very serious situation regarding Russia’s build-up of troops on the border with Ukraine,” explained Danish Foreign Minister Jeppe Kofod. “It threatens European security.”
The Danish Minister of Defense, Trine Bramsen, added that the move was intended as “a very clear signal to Russia.”
The Danish F-16 detachment will be deployed to Lithuania, which makes a lot of sense as it means that Denmark will have military deployed to all three Baltic countries: F-16 in Lithuania, divisional HQ staff in Latvia and eFP mechanised infantry company in Estonia. Plus a frigate
There has been speculation that the three Baltic Fleet landing ships could be headed for the Black Sea. Last year, the waters around the Russian-occupied Crimean peninsula were subject to some tense standoffs between the Russian Navy and NATO warships. Since then, the overall security situation has become more uneasy, with the steady influx of Russian troops and materiel to the border areas adjacent to Ukraine, including Crimea. The result has been fears of a potential invasion of Ukraine, an issue that was at the top of the agenda during recent talks between Russian and Western officials that ended in a stalemate. And, should an invasion of Ukraine via the southern route manifest itself, the Black Sea Fleet would be almost certain to carry out an amphibious landing in the Sea of Azov. The arrival of two large landing ships would provide a significant addition to the Black Sea Fleet’s existing resources.

Ropucha class landing ships were involved in this firepower demonstration in Russian-occupied Crimea back in 2016., YOUTUBE SCREENCAP
Added to this is the factor of upcoming exercises involving Russia and its close ally Belarus, which also borders Ukraine. Russian forces have begun to arrive in Belarus for the maneuvers, which do little to address the soaring tensions between Moscow and the West over Ukraine.
In the past, there have been predictions that a new Russian invasion of Ukraine could well involve troops arriving across the Belarusian border.
The latest series of Russian/Belarusian drills significantly takes place along the latter country’s southern and western borders, adjacent to both Ukraine and NATO member Poland.
The movement of the Baltic Fleet ships could also be a straightforward transfer of assets, with the three Ropuchas from Baltyysk now sailing to the Kola Peninsula to take the place of the three Northern Fleet landing ships now in the Baltic.
Another option could involve the transfer of the Baltic Fleet Ropuchas to Russia’s port of Tartus on Syria’s Mediterranean coast. This port has played an important role since Moscow launched its Syrian campaign in 2015, receiving a steady stream of vessels bringing cargoes from Russia.
Whether headed for the Black Sea or the Mediterranean, these routes would almost certainly see the Ropuchas transit through the English Channel, alerting the interests of the British Armed Forces.
In the past, Russian Navy warships passing through this body of water have received close attention from Royal Navy vessels and from Royal Air Force aircraft alike.
Whatever the ultimate destination of the Ropuchas, it’s a reflection of the highly strained relations that currently exist between Moscow and the West.
At this point, with rhetoric soaring on all sides, and with no clearly defined end-game to Russia’s apparent brinksmanship around Ukraine’s borders, a movement of warships that might have been viewed as fairly routine during less uncertain times is now cause for some consternation.
Update, 1.45 PM PST: This article was amended to reflect the fact that Royal Danish Air Force F-16s will be deployed to Šiauliai Air Base in Lithuania. The base is currently also housing a rotational detachment of Polish Air Force F-16s.
Update, 6.00 AM PST: The three Russian Navy landing ships that had remained in the Baltic Sea have now also left these waters, following the same route as the previous three vessels, as evidenced by the following photographs, taken as they passed through the Great Belt earlier today.
The vessels involved in this latest movement are the Northern Fleet’s Ropucha class vessels Olenegorskiy Gornyak and Georgiy Pobedonosets and the Ivan Gren class landing ship Pyotr Morgunov. We will continue to track the progress of all six vessels..















